Table of Contents
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept- it’s the backbone of tools we use every day, from personalized recommendations on Netflix to virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. But with great power comes great responsibility. As designers, our role is to ensure that these AI-powered interfaces are not only functional but also empathetic, inclusive, and easy to use. Human-Centered Design (HCD) ensures that AI serves humans, not the other way around.
This blog explores how HCD principles can make AI experiences accessible, intuitive, and trustworthy while addressing the unique challenges of designing for this advanced technology.

The Role of Human-Centered Design in AI
At its core, Human-Centered Design puts users first. This approach becomes even more critical with AI, where the complexity of algorithms can sometimes alienate users. The objective is to strike a balance between innovation and usability by focusing on:
- Empathy-driven solutions: Understanding the “why” behind user needs and creating AI systems that genuinely solve problems.
- Transparency in decision-making: Helping users trust AI by demystifying how it works.
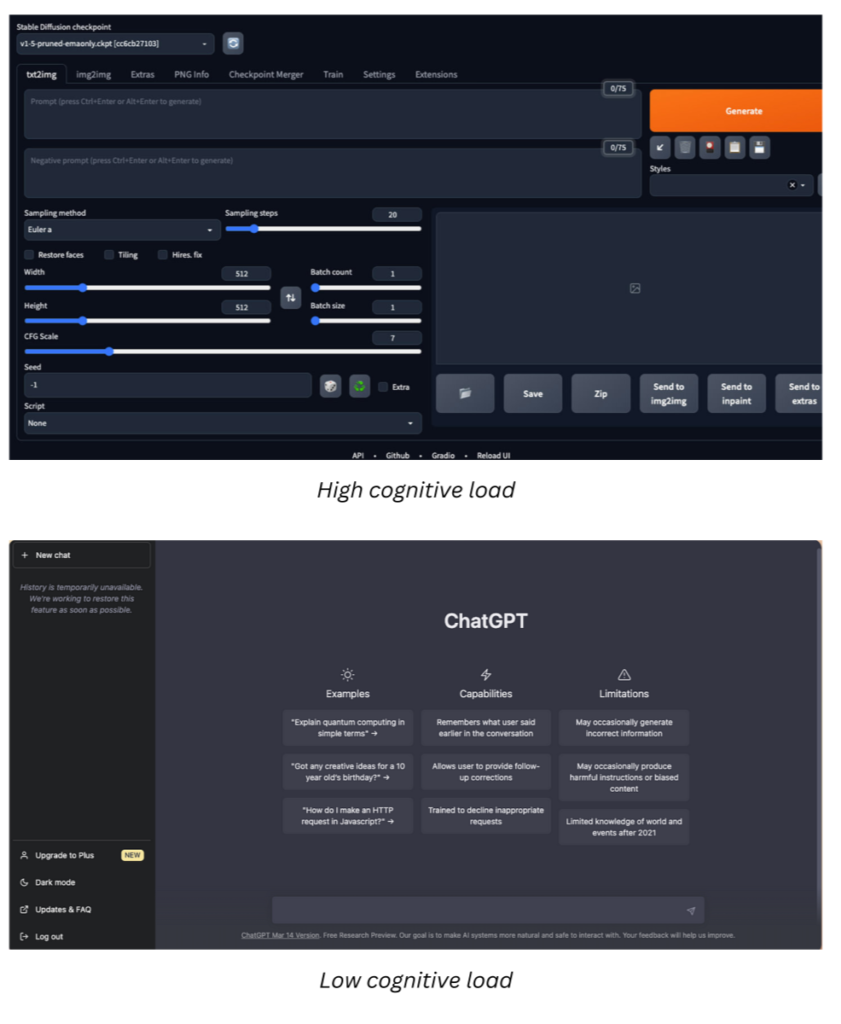
- Minimizing cognitive overload: Presenting insights in digestible formats, ensuring users don’t feel overwhelmed by technical jargon or data-heavy visuals.
For example, consider a financial planning app that uses AI to predict spending habits. A human-centered approach would include clear explanations of predictions, simple visuals to represent trends, and actionable recommendations.
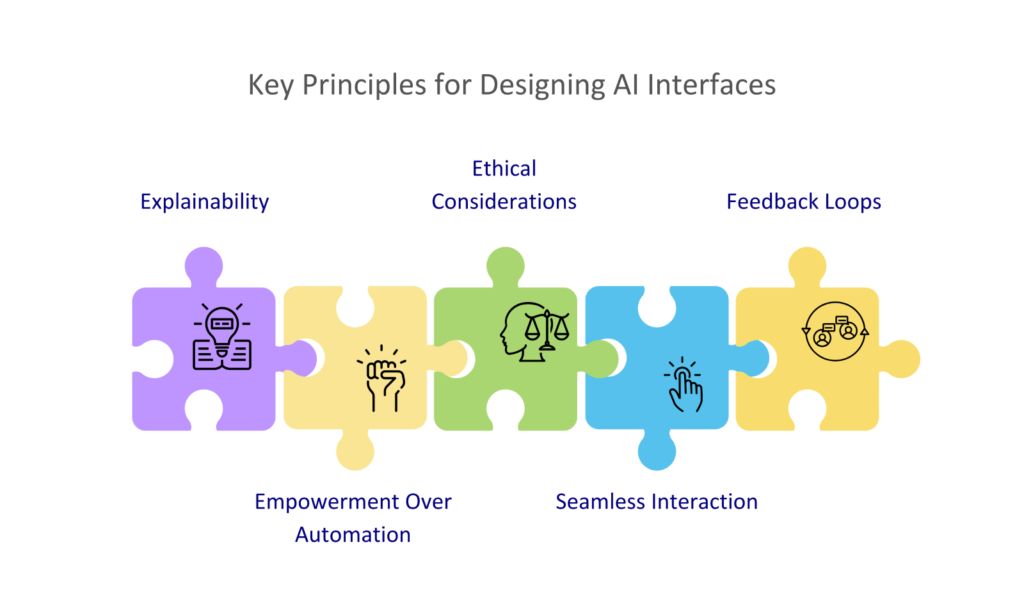
Key Principles for Designing AI Interfaces
Explainability
Users need to understand AI’s logic. For example, if an AI-powered hiring tool rejects a candidate, it should provide clear reasons, like “insufficient project experience” or “skills mismatch,” rather than leaving the user guessing.
Empowerment Over Automation
AI should supplement human decision-making, not replace it. For instance, an AI-driven photo editing tool could suggest enhancements (e.g., lighting adjustments or background changes) while allowing users to override or customize these suggestions.
Ethical Considerations
AI should be free of biases. Testing with diverse user groups ensures the system remains inclusive. For instance, facial recognition software should work equally well for all skin tones.
Seamless Interaction
Natural interactions through voice, gestures, or predictive responses make AI interfaces feel more intuitive. Think of a smart home assistant that understands a user’s preferences over time and adjusts lighting or temperature without explicit commands.
Feedback Loops
AI systems should enable users to give feedback, helping the system learn and improve. A ride-hailing app, for instance, could ask users to rate the accuracy of estimated arrival times, fine-tuning predictions for future rides.
Challenges in Human-Centered Design for AI
Despite its advantages, designing human-centered AI interfaces comes with unique challenges:
- Trust Building: Users can be skeptical of AI, especially when it makes mistakes or lacks transparency. For instance, a health app that provides AI-generated diagnoses must work extra hard to ensure users feel confident in its accuracy.
- Privacy Concerns: AI relies on large datasets to function effectively, but users often worry about how their data is collected and used. Designers must prioritize features like data anonymization and user-controlled privacy settings.
- Avoiding Over-Personalization: While personalization enhances user experiences, excessive tailoring can feel invasive. For example, a shopping app suggesting items based on private conversations could breach user trust.
- Complexity of Predictive Systems: AI can’t always predict human behavior accurately, leading to frustration when the system fails to meet expectations. Designers must account for these edge cases and offer easy-to-access alternatives.
Real-World Applications of Human-Centered AI
- Healthcare
AI-powered diagnostic tools like IBM Watson Health provide actionable insights to doctors while presenting information in a patient-friendly language. This ensures that complex medical data is accessible to users without overwhelming them. - E-commerce
Platforms like Amazon use AI for personalized recommendations. By providing filters and customization options, users can fine-tune suggestions, making the experience both efficient and empowering. - Education
AI tutors like Duolingo adapt to individual learning styles, offering targeted exercises and real-time feedback. This personalized learning ensures students stay motivated while achieving their goals. - Customer Support
Chatbots powered by AI are becoming the first line of customer interaction. Human-centered designs ensure these bots feel conversational, provide clear resolutions, and escalate issues to humans when necessary.
AI in Healthcare
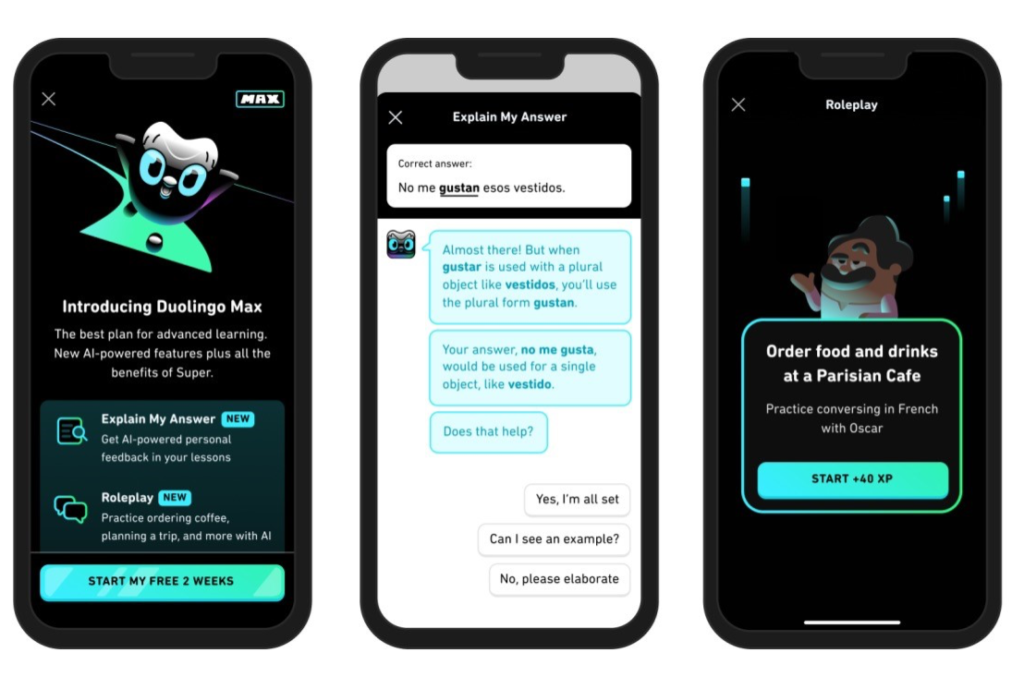
AI in Learning
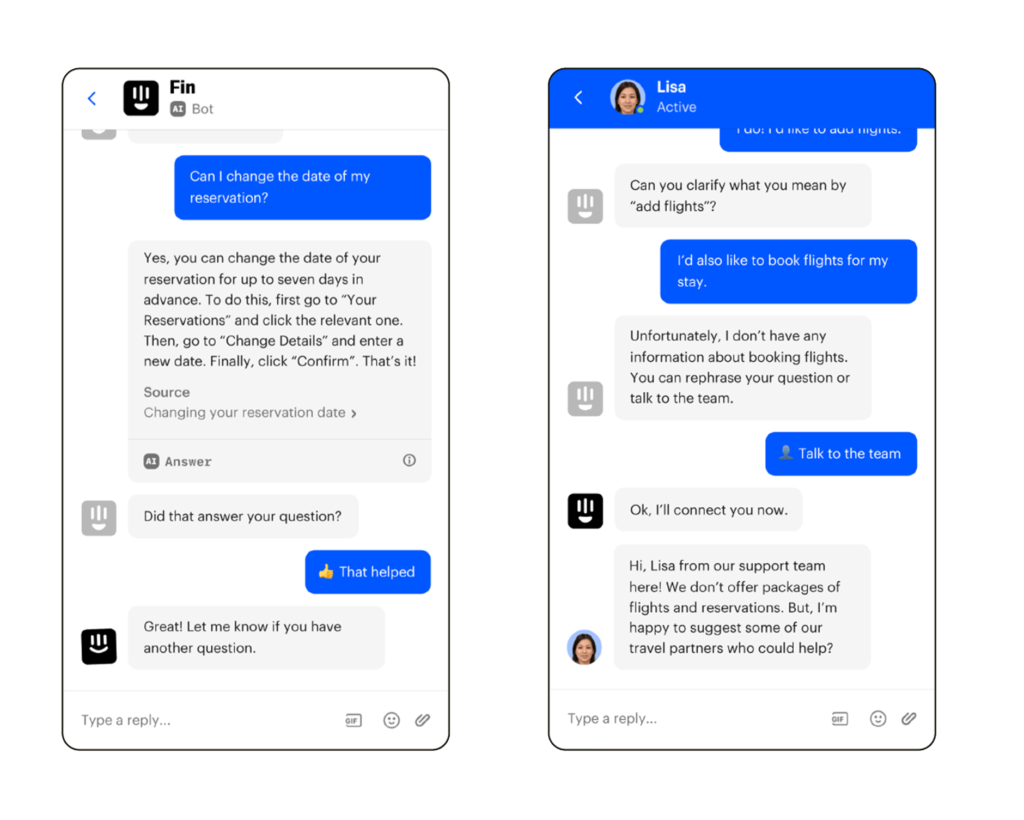
Customer Support AI Chatbot
Best Practices for Designing AI-Powered Interfaces
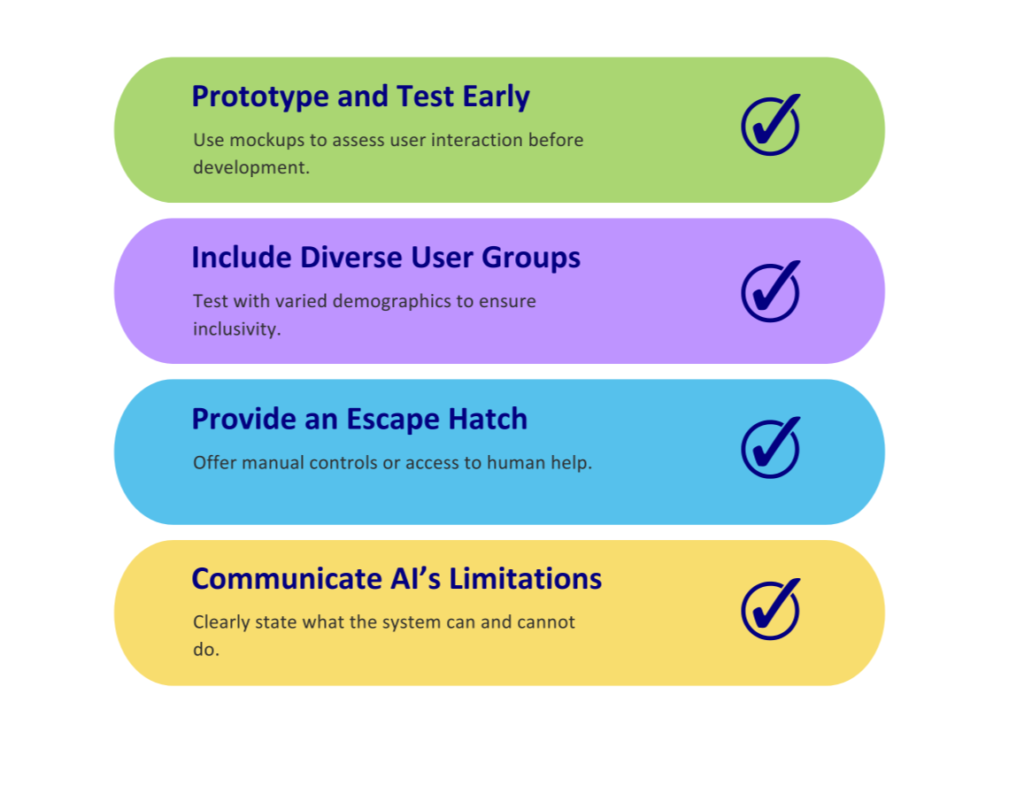
Here are actionable tips for creating user-friendly AI systems:
- Prototype and Test Early: Use mockups to evaluate how users interact with AI features before committing to development.
- Include Diverse User Groups: Ensure inclusivity by testing across demographics, languages, and accessibility needs.
- Provide an Escape Hatch: Always give users an option to revert to manual controls or access a human representative.
- Communicate AI’s Limitations: Be upfront about what the system can and cannot do to manage user expectations effectively.
Looking Ahead
As AI continues to evolve, the need for human-centered design will become more critical. By prioritizing empathy, trust, and inclusivity, designers can ensure that AI becomes a tool for empowerment rather than alienation. The future lies in intelligent systems that not only understand data but also understand the people they serve.